Transport in supported liquid membranes:
In the extraction of the metal ions, a carrier molecule within the membrane picks up metal ions from the feed solution creating a complex. This complex diffuses to the other side of the membrane whereas decomplexation occurs and the metal ions are released within a receiving phase. Free carrier after that diffuses back across the membrane for use in another cycle. This coupled transport by SLM can take place through the following processes.
* Co-transport
* Coupled transport
Coion transport in which both metal ions and its counterions are transported from the feed solution through the SLM and into the receiving phase is shown in Figure (a). Here If the carrier, C, is neutral, a driving force is the difference within distribution coefficients (Kd) among the feed and receiving solutions. This is generally achieved by maintaining a concentration gradient of the counterion X- between the two explanations. This metal ion and counterion form a complex along with the carrier, C, in the membrane. That complex diffuses to another side of the liquid membrane and the metal ion and counterion are released within the receiver solution. A chemical reaction for this coupled transport is
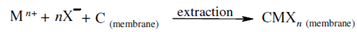
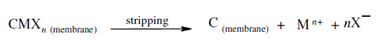
A liberated carrier molecule diffuses back to the feed solution -SLM interface, picks up another metal ion and the counterion and the process continues until the final equilibrium is attained.