Counterion transport:
Counterion transport in which an acidic carrier, HC, loses a proton and creates a complex, MC, metal ion at the feed solution-SLM interface. That complex diffuses to the SLM-strip solution interface while it liberates a metal cation within the receiver phase and concurrently picks up a proton from the strip solution. The reproduced carrier, HC, diffuses back to the feed solution-SLM interface, picks up the other metal ion and the procedure continues. An acidic carrier molecule shuttles among the feed and the strip solution-SLM interfaces.
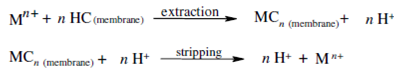
The driving force within a counter transport SLM system is the pH difference among the feed and the strip solution. For capable transport, high feed and low strip solution, Kd values are required. The Kd difference among the feed and strip solution is managed through a pH gradient. To divalent metal ion and an acidic carrier, the reaction at the feed solution-SLM interface is as follows:
M2+ + 2 HC → MC2 ( membrane ) + 2 H+ (aq)