Flame Ionisation Detector (FID):
Within operation as the solute elutes from the column, it is mixed along with hydrogen and then combusted. In the combustion procedure, transitional ions are created that could be collected through a metal conductor.
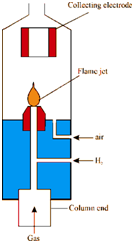
Figure: Principle and structure of flame ionisation detector
These collected ions cause an electronic signal that could be amplified and displayed on a recorder. Ideally, the last combustion products are carbon dioxide and water so in which they could be safely vented to the atmosphere. The number of these transitional ions created is proportional to the total number of solute molecules passing by the detector. The FID will respond to organic compounds just i.e., those solutes which have a carbon-hydrogen bond and are combustible. Table 7.4 lists the solutes for that FID does not respond. The lack of response to air and water makes the FID especially suitable for the analysis of air pollutants or aqueous samples like as alcoholic beverages, biological materials etc. Same, the absence of a "solvent peak" makes carbon disulphide a convenient solvent for use along with the FID.