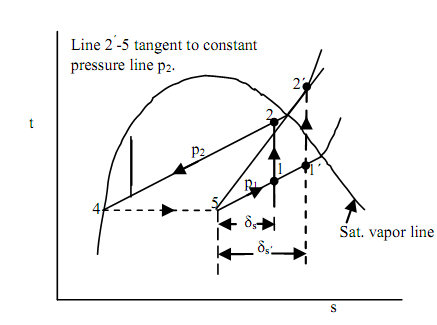
Ewing's Method For Suction State With Respect To Maximum Cop:
The COP of a easy vapour compression system can be attained close to that of the ideal value by utilizing (a) an suitable refrigerant and (b) choosing operating limits as close to each other as possible. The Ewing's method is depends on the fact that like the point of compression proceeds away from state 5, the COP enhanced. If the compression begins right from state 5, the COP would be zero. Referring to the figure, we illustrate that COP is:
Cop = (h1-h4)/(h4-h1)=T1δs/(h2-h4-T1δs)
=T1/ [(h2-h4)/δs-T1]
The slope (h2 - h4)/δs will be minimum equivalent to the tangent to the condensing pressure line.
COP max = T1 [{h2-h4)/δ s}min - T1]
The quantity [(h2-h4)/δs)]min is found out by sketch a line from state 5, tangent to constant pressure line p2. In the current case, this minimum value is
[(h2-h4)/δs]min=(h2-h4)/(S1-S5)'
Because in high speed compressors in wet compression this would not be possible to evaporate tiny liquid droplets, Ewing's technique is no longer used. Therefore, the performance not only would not match that stated above, however there would also be serious mechanical problems.
Ewing's Diagram