Applications
Although ionic model calculations do not always give correct predictions of lattice energies (and particularly when the approximate Kapustinskii equation is employed) the trends predicted are generally reliable and can be used to rationalize many observations in inorganic chemistry.
(i) Group oxidation states
The occurrence of ions like Na+, Mg2+ and Al3+ depends on the balance among the energies needed to form them in the gas phase and the lattice energies that stabilize them in solids. Refer magnesium. The gas-phase ionization energy (IE) needed to form Mg2+ is considerably greater than for Mg+. Though, the lattice energy stabilizing the ionic structure MgF2 is much larger than that of MgF and amply compensates for the additional IE. It is feasible to estimate lattice energy of MgF, and (depending on what assumptions are employed about the ionic radius of Mg+) its formation from the elements might be exothermic. Though, the enthalpy of formation of MgF2 is predicted to be much more negative and the reason why MgF(s) is not known is that it spontaneously disproportionates:
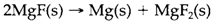
Ionization further than the closed-shell configuration Mg2+ involves the removal of a much more tightly bound 2p electron. So the third IE is very large and can never be compensated by the extra lattice energy of a Mg3+ compound.
(ii) Stabilization of high and low oxidation states
While an element has variable oxidation states, it is frequently found that the highest value is obtained with oxide and/or fluoride. The ionic model once again suggests that a balance among IE and lattice energy is significant. Small and/or highly charged ions give the highest lattice energies as per the Equation 1, and the raise in lattice energy with higher oxidation state is more supposed to compensate for the high IE. By difference, a large ion with low charge like I- is more likely to stabilize a low oxidation state, like the smaller lattice energy may no longer compensate for high IE input. So CuF is not known but the other halides CuX are. most probably the lattice energy increase from CuF to CuF2 is enough to force a isproportionation like that of MgF but this is not so with larger halide ions. By difference, CuX2 is stable with the X=F, Cl and Br, but not I.
(iii) Stabilization of large onions or cations
It is a helpful rule that large cations stabilize large anions. Oxoanion salts like carbonates are harder to decompose thermally when combined with large cations. It is also found that solids in which both ions are large are usually less soluble in water than ones with a large ion and a small one. These trends are occasionally erroneously ascribed to 'lattice packing' influences, with the implication that two large ions jointly have a larger lattice energy than a small and a large ion. Theoretical/hypothetical (and experimental) estimates of lattice energies contradict this view and a satisfactory description depends on a balance of energies. Refer the decomposition of a group 2 metal carbonate MCO3:
Figure 2 depicts a thermochemical cycle, that predicts that the enthalpy change in this reaction is
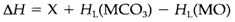
In which X is enthalpy input needed for the gas-phase decomposition of CO32-and HL are the lattice enthalpies. X is positive, but as per the Equation 1 the lattice energy of MO will all the time be larger than that of MCO3 since the oxide ion is smaller. The variation of lattice energies in Equation 2 therefore provides a negative contribution to the entire ΔH. If we have a larger M2+ ion, both lattice energies become smaller, but the significant thing is that their variation becomes smaller. So smaller M2+ provides a less endothermic decomposition reaction so, that is possible at a lower temperature.
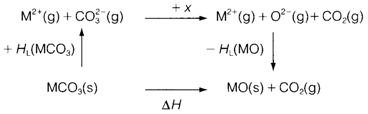
Fig. Thermochemical cycle for the decomposition of MCO3.