D′Alembert's Principle - Application to a Particle:
By the use of this principle, difficult problems of dynamics can be reduced to simpler problems of statics.
Consider a particle P illustrates in Figure (a). A force F is acting upon this particle. The acceleration of the particle can be attained by the equation:
F = ma
where, m is the mass of the particle in which F produces on acceleration a. This equation can be written as
F - ma = 0 or F + Fi = 0
where, vector Fi = - ma is termed as inertia force, and it is always directed opposite to the acceleration a of the particle (Figure
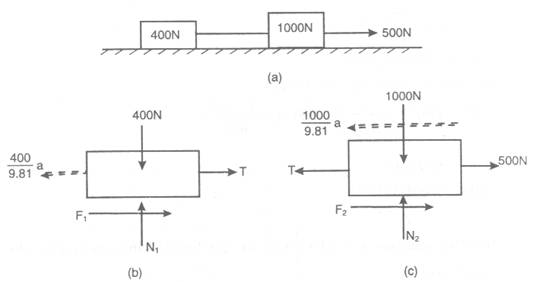
This also may be described as discussed below :
A force F is acting on a particle P, and inertia force Fi = - ma is imagined to be also acting on the particle. Then F and Fi are in equilibrium. It is known as D'Alembert's principle.
When F and Fi act on a particle, the same shall remain in equilibrium. To distinguish this equilibrium from static equilibrium it is termed as dynamic equilibrium.
When a number of forces are acting on the particle, the principle can be applied as discussed below. Let F1 , F2 , . . . , Fn be the forces acting on a particle P as illustrated in Figure (a). We may calculate the resultant force R of the system. Then we may write R = ma, where a shall give the resultant acceleration of the particle.
This equation may be written as
R - m a = 0 or R + Fi = 0
where, Fi = - m a is the inertia force.