Lower Pair:
While connection among two elements is through the area of contact, that means there is surface contact among the two links, the pair is known as lower pair. Examples include motion between crank pin, motion of slider in the cylinder and connecting rod at big end.
Revolute or Turning Pair (Hinged Joint)
A revolute pair is shown in given figure. It is seen that this pair permits only a relative rotation among elements 1 and 2 that can be expressed by a single coordinate 'θ'. Therefore, a revolute pair contains a single degree of freedom.
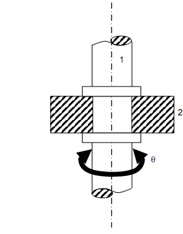
Revolute or Turning Pair
As shown in below figure, a prismatic pair permits only a relative translation among elements 1 and 2, that can be expressed by a single coordinate 's', and it contain one degree of freedom.
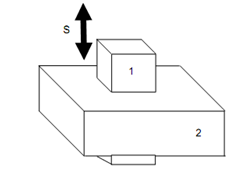
Prismatic or Sliding Pair
As illustrated in given figure, a screw pair permits rotation as well as translation but these two movements are associated to each other. Thus, screw pair contains one degree of freedom because the relative movement among 1 and 2 may be expressed by a single coordinate 'θ' or's'. These two coordinates are associated by the following relation:
Δθ / 2π = Δ s/L
here, L is lead of the screw.
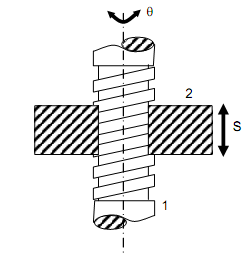
Screw Pair
As illustrated in figure, a cylindrical pair permits both rotation & translation parallel to the axis of rotation among elements 1 and 2. These relative movements may be expressed by two independent coordinates 'θ' or's' because they are not associated with each other. Degrees of freedom in this case are equivalent to two.
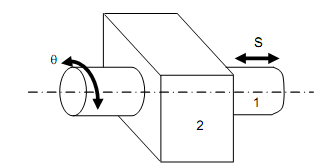
Cylindrical Pair
A ball & socket joint, as illustrated in figure, forms a spherical pair. Any rotation of element 2 relative to 1 may be resolved in the three components. Thus, the complete description of motion needs three independent coordinates. Two of these coordinates 'α' & 'β' are needed to indicate the position of axis OA and the third coordinate 'θ' explained the rotation around the axis of OA. This pair contains three degrees of freedom.
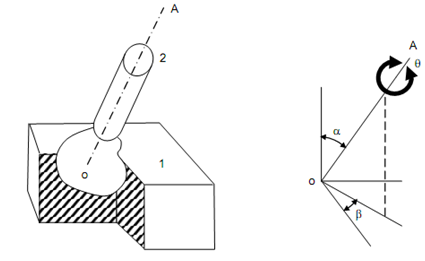
Spherical Pair
A planar pair is illustrated in given figure. The relative motion among 1 and 2 can be explained by x and y coordinates in x-y plane. The x and y coordinates defined relative translation and θ defined relative rotation around z-axis. This pair contain three degrees of freedom.
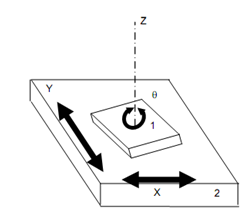
Planar Pair