Degree Of Freedom:
The degree of freedom of a body is equivalent to the number of independent coordinates needs to specify the movement. For a cricket ball while it is in air, six independent coordinates are needed to specify its motion. Three independent displacements coordinates along the three axes (x, y, z) & three independent coordinates for rotations regarding these axes are needed to describe its motion in space. Thus, degrees of freedom for this ball are equivalent to six. If this cricket ball moves on the ground, this movement may be described by two axes in the plane. Two independent displacement coordinates (x, y) and one independent coordinate for rotation regarding vertical axis are needed, to account for linear displacement in x, y directions & rotation θ.
While the body contain a plane surface to slide on a plane, the rotation around x and y-axes will be removed but it can rotate around an axis perpendicular to the plane that means z-axis.
At the similar time, while executing plane motion, this body undergoes displacement which may be resolved along x & y axis. The rotation around z-axis and components of displacement along x & y axes are independent of each other. Thus, a sliding body on a plane surface contain three degrees of freedom. The plane surface imposes constraints on the sliding body. It means application of constraints on the motion of body drop off degrees of freedom.
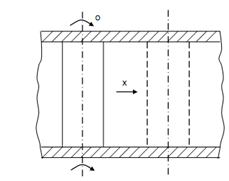
These were the instance of unconstrained or partially constrained bodies. If a cylinder rolls without sliding along with a straight guided path, the degree of freedom is equivalent to one just because rotation in case of pure rolling is based on linear motion. It is a case of entirely constrained motion.
The angle of rotation θ = x/ r here, r is radius of cylinder and x is linear displacement.
Degree of Freedom
Completely Constrained Motion
Describe partially constrained, completely constrained, and unconstrained motion. Also cite two instances for each type of motion.