Minimizing Gamma Influence with Boron Coating Area:
Ionization chamber sensitivity to gamma rays could also be decrease through increasing chamber sensitivity to neutrons. This is complete through increasing the boron-coated area, as display in Figure. Both ionization chambers display in Figure have the similar sensitive volume.
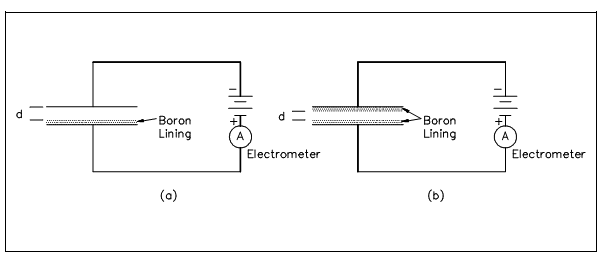
Figure: Minimizing Gamma Influence with Boron Coating Area
The ionization chamber in Figure has double the boron area as the ionization chamber in other figure. The result is which more neutron-induced alpha particles are generates, and neutron sensitivity is rise. Ionization chambers supplied commercially are designed for minimize gamma sensitivity through both of the methods elaborates previously. Gamma sensitivity could be minimized but not eliminated. To reactors operating near peak power, neutrons are the dominant radiation and almost all of the current is because of neutrons. Those chambers are used at high reactor powers and are referred to as uncompensated ion chambers. The uncompensated ion chamber is not appropriate for use at intermediate or low power levels since the gamma response at these power levels could be significant compared to the neutron response.