File System Organization (Directory Hierarchy)
Directories are special files which holds names of other sub-directories and files. Classical directory structure of the Unix system consists of the subsequent directories: -
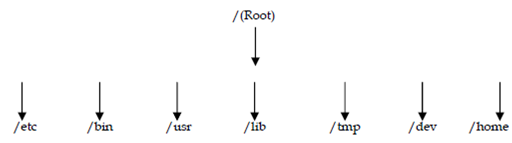
Figure
The top level directory is known as the root directory and is indicated via a single / (forward slash). Whole the directories and files belong to the root directory.
There are following are the list of standard directory names in the Unix file system.
/ Root directory. This is the parent of all the directories and files in the Unix file system.
/etc System configuration files and executable directory. Many of the administrative, command-related files are stored here.
/bin Command-line executable directory. This directory holds all the Unix native command executables
/usr Architecture independent and architecture dependent sharable files
/lib The library files for several programming languages like as C are stored in this directory
/tmp This directory is used for not a permanent storage or the temporary storage of files
/dev Device directory containing special files for character- and block-oriented devices such a printers and keyboards. File called null existing in this directory is called the bit bucket and can be used to redirect output to nowhere
/home This directory holds data which is specific to an individual user