Structured programming (Pascal and C)
Structured programming is evolved as a mechanism to address the growing issues of programming in the large. Superior programming projects consist of large development teams, developing various parts of the similar project independently. Figure shows Programs consist of multiple and in turn every module has a set of functions of associated types.
- Structured programming is based on the algorithm rather than data
- Programs are separated into individual modules which perform various task.
- Controls the scope of data
- Support modular programming
- Overview of user defined data types
Technically, a structured language allows procedures and functions to be declared inside other functions or procedures, and thus cannot formally be known as a block- structured language. Therefore, it is referred to as structured languages such as Pascal, ALGOL and the likes.
Structured programming permits compartmentalization of data and code. This is a unique feature of any structured language. This programming language refers to the ability of a language to section off and hides all information and instructions necessary to perform a specific task from the rest of the program. Code could be compartmentalized in C++ by using functions or code blocks. The Functions are used to define and code separately, a special tasks needed in a program. This permits programs to be modular. A Code block is a logically connected group of program statements which is treated such as a Unit
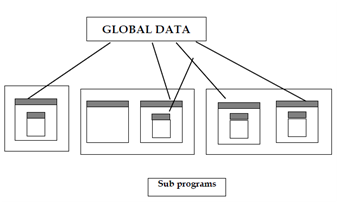
Module 1 Module 2 Module3
Figure: Structured Programming