The Reverse Biased pn-Junction (Diode)
While positive terminal of a battery is attached to N-side or the cathode and negative terminal to the P-side or the anode of a diode (PN-junction), the diode is called up to be REVERSED - BIASED.
A PN-junction diode is reverse biased while the n type material (cathode) is more positive than the p type (anode). This is cause of the depletion region to broaden and stop current. A diode shall not conduct while the arrow points to the more positive of the diode potentials.
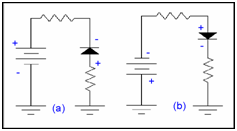
In diagram (a) negative of the battery is linked to the anode via a resistor and positive terminal of the battery is attached the cathode so no current will pass and we may say that diode is not get existing and it will behave as an open circuit.
In diagram (b) the negative terminal of the battery is attached to the anode through a resistor & positive terminal of the battery is attached the cathode.
The reverse - biased diode acts opposite to the forward-biased diode. It means in the case of a reverse-biased diode, majority carrier current does not pass and instead of that single minority carrier current can pass. Furthermore, the depletion charge layer will enlarged or expand compared to the forward -biased diode whereas the depletion charge layer get shrinks, so it will behave as an open circuit.
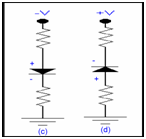
In diagram (c) the negative voltage is applied to the anode of the diode by a resistance & cathode terminal of the diode is attached to the neutral terminal by resistance. Which will fulfil the condition of reversed biased.
In diagram (d) the positive voltage is applied to the cathode of the diode through a resistance & anode terminal of the diode is attached to the neutral terminal via resistance. That will fulfil the condition of reversed biased
Here we may say that the reverse-biased PN-junction can't support majority carrier current but this will permit the minority carrier current to pass across the junction. This minority carrier current is said as reverse current and it is much smaller than the forward majority carrier current of a forward biased PN-junction.