Iterative Analysis
A simple iterative process, as indicated in the following example
EXAMPLE: Determine the current ID and the diode voltage VD for the circuit in the fig. with VDD = 5volts and R =1k. Suppose that the diode contain a current of 1mA at a voltage of 0.7V & its voltage drop modify by 0.1V for every decade modification in current.
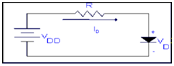
SOLUTION:
To start the iteration, we suppose that VD = 0.7V and the equation (ii) find out the current
ID = VDD - VD/R
= 5 - 0.7/1= 4.3mA
From our earlier knowledge
V2 - V1 = nVTln(I2/I1)
The eq of log to the base 10 form will be like
V2 - V1 =2.3nVTlogI2/I1
In this case, 2.3 nVT = 0.1V
V2 = V1 + 0.1logI2/I1
Putting V1 =0.7V, I1 =1mA and I2 =4.3mA we get
V2 = 0.763V
Therefore the results of the first iteration are
ID =4.3mA & VD =0.763 V
The second iteration proceeds in the same manner
ID = VDD - VD/ R
where VD = 0.763 V
ID = 5 - 0.763/1= 4.237mA
V2 = 0.763 + 0.1 log(4.237/4.3) = 0.762 V
Therefore the second iteration yields
ID = 4.23mA & VD = 0.762V
As these values are not much very different from the values gets after the first iteration, no additional iterations are essential and the
Solution is ID = 4.23mA & VD = 0.762V