Inheritance
Inheritance is the process through that object of one class obtains the properties of objects of another class. An Inheritance supports the concept of hierarchical classification. For instance, the bird robin is a category of the class flying bird that is again a category of the class bird. As described in Figure the principle behind this sort of division is that every derived class shares common features with the class from that it is derived.
Within OOP, the concept of inheritance gives the idea of reusability. This means in that we can add further characteristics to an existing class without changing it. This is possible through deriving a new class from the existing one. A new class will have the combined features of both the classes. Therefore the real appeal and power of the inheritance mechanism is which it permits the programmer to reuse a class that is almost, but not exactly what he requires and to tailor the class in such a way that it does not introduce any undesirable side effects into the rest of the classes. Within Java, the derived class is known as subclass.
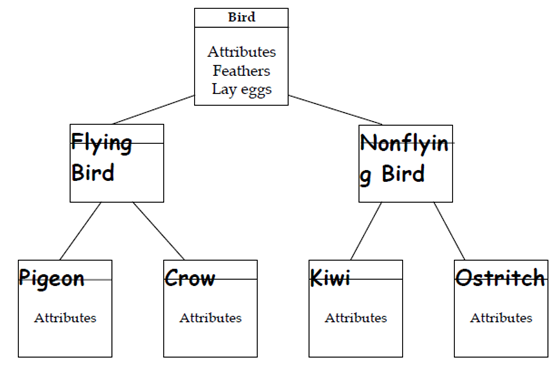
Figure: Property of Inheritance
// Sample program for inheritance
//source file: inheritance.cpp
class building
{
int rooms; int floors; int areas;
public:
void set_rooms(int num);
int get_rooms();
void set_floors(int num);
int get_floors();
void set_area(int num);
int get_area();
};
class home:public building // class home is the inherited class of building
{
int bedrooms;
int baths;
public:
void set_bedrooms(int num);
int get_bedrooms();
void set_baths(int num);
int get_baths();
};
void building::set_rooms(int num) //the function definition part
{
rooms = num;
}
int building:: get_rooms()
{
return rooms;
}
void building::set_floors(int num)
{
floors = num;
}
int building::get_floor()
{
return floors;
}
void building::set_area(int num)
{
area = num;
}
int building::get_area()
{
return area;
}
void home::set_bedrooms(int num)
{
bedrooms = num;
}
int home::get_bedrooms()
{
return bedrooms;
}
void home::set_baths(int num)
{
baths = num;
}
int home::get_baths()
{
return baths;
}
void main()
{
home h1; h1.set_rooms(10);
h1.set_floors(5);
h1.set_bedrooms(10);
h1.set_baths(5);
h1.set_area(950);
cout<<"number of rooms"<<h1.get_rooms();
cout<<"number of floors"<<h1.get_floors();
cout<<"number of bedrooms"<<h1.get_bedrooms();
cout<<"number of baths"<<h1.get_baths();
cout<<"area of a home"<<h1.get_area();
return 0;
}
The given above example clearly states the concept of inheritance. Because class home is the inherited class of building it could able to access the building class members (base class) and its member functions.