Isoenzymes
Isoenzymes (isozymes) are various forms of an enzyme that catalyze the similar reaction, but that exhibit several kinetic or physical properties, like as isoelectric point, pH optimum, substrate affinity or effect of inhibitors. Several isoenzyme forms of a given enzyme are commonly derived from various genes and frequently occur in several tissues of the body.
An instance of an enzyme that has many isoenzyme forms is LDH (lactate dehydrogenase) that catalyzes the reversible conversion of pyruvate into lactate in the presence of the coenzyme NADH. Lactate dehydrogenase is a tetramer of two various kinds of subunits that is called H and M, that have small
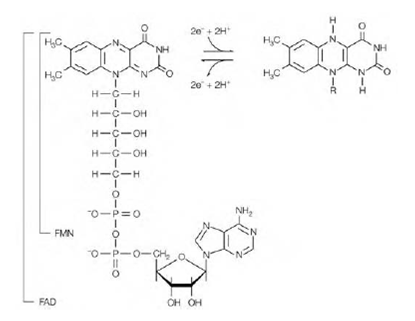
Figure: The structures of the coenzymes FAD and FMN.
differences in amino acid sequence. The two subunits can merge randomly with every other, forming five isoenzymes which have the compositions H4, H2M2, H3M, M4 and HM3. The five isoenzymes can be determined electrophoretically. M subunits predominate in skeletal muscle and liver while H subunits predominate in the heart. H3M and H4 isoenzymes are mainly found predominantly in red blood cells and the heart ; H2M2 is found predominantly in the brain; while HM3and M4 are found predominantly in the liver and skeletal muscle. Therefore, the isoenzyme pattern is characteristic of a particular tissue a factor which is of immense diagnostic importance in medicine. Infectious hepatitis myocardial infarction and muscle diseases includes cell death of the affected tissue with free of the cell contents into the blood. As lactate dehydrogenase is a soluble, cytosolic protein it is readily free in these situation. In the normal circumstances there is little lactate dehydrogenase in the blood. Therefore the pattern of lactate dehydrogenase isoenzymes in the blood is indicative of the tissue that released the isoenzymes and so can be used to diagnose a condition and to monitor the progress of treatment. Infarction additionally to the pattern of lactate dehydrogenase isoenzymes for the clinical diagnosis of a myocardial, other enzymes, including creatine kinase and aspartate aminotransferase are routinely measured, along with an ECG (electrocardiogram).