Enzyme classification
Several enzymes are named through adding the suffix ‘-ase’ to the name of their substrate. Therefore urease is the enzyme which catalyzes the hydrolysis of urea and 6-bisphosphatase hydrolyzes fructose-1, fructose-1, and 6-bisphosphate. Moreover, other enzymes, like as chymotrypsin and trypsin , have names which do not indicate their substrate. Some enzymes have various another names.
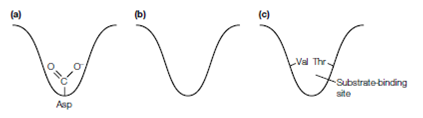
Figure: Schematic representation of the substrate-binding sites in the serine proteases (a)trypsin, (b) chymotrypsin and (c) elastase.
To rationalize enzyme names, a system of enzyme nomenclature has been internationally approved. This system wills places all enzymes into one of six major classes based on the kind of reaction catalyzed. Each enzyme is then distinctively identified with a four-digit classification number. Therefore trypsin has the Enzyme Commission (EC) number 3.4.21.4, where the first number (3) indicates in which it is a hydrolase, the second number (4) which it is a protease which hydrolyzes peptide bonds, the third number (21) that it is a serine protease with a critical serine residue at the active site and the fourth number (4) denote that it was the fourth enzyme to be assigned to this class. For contrast, chymotrypsin has the Enzyme Commission number 3.4.21.1 and elastase 3.4.21.36.
