Coenzymes and prosthetic groups
Several enzymes need the presence of little and nonprotein units or cofactors to carry out their particular reaction. The Cofactors may be either one or more inorganic ions, like as Zn2+or Fe2+ or a hardly organic molecule which is known as coenzyme. A metal or coenzyme which is covalently attached to the enzyme is called a prosthetic group (cf. heme in hemoglobin.A complete catalytically-active enzyme together with its metal or coenzyme ion is called a holoenzyme. The protein category of the enzyme on its own without its cofactor is termed an apoenzyme.Many coenzymes, like as NAD , are bound and released through the enzyme during its catalytic cycle and in effect function as cosubstrates. Several coenzymes are derived from vitamin precursors which is described in the Table 2 that are frequent essential parts of the organism’s diet, therefore giving increment to deficiency diseases when in inadequate supply.
NAD (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) and NADP (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate ) coenzymes are based on a general structure consisting of the base adenine two ribose sugars linked through phosphate groups and a nicotinamide ring . NADP is different from NAD in having an additional phosphate group attached to one of the ribose sugars. Both two coenzymes share a common function as they both act as carriers of electrons and are included in oxidation–reduction reactions. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is more generally used in catabolic (breakdown) reactions, whilst adenine dinucleotide phosphate is used in anabolic (biosynthetic) reactions. The reactive category of both molecules is the nicotinamide ring that exists in either a reduced or an oxidized form and so acts to accept or donate electrons in an enzymic reaction. The reaction also includes the transfer of protons according to the equation:
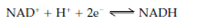
FAD (Flavin adenine dinucleotide) and FMN (flavin mononucleotide) are also carriers of electrons and have related chemical structures that are described in above figure. Both of these coenzymes consist of a flavine mononucleotide unit that contains the reactive site. Flavin adenine dinucleotide has an additional sugar group and an adenine base which complete its structure. Flavin adenine dinucleotide and fiavin mononucleotide react with two protons as well as two electrons in alternating among the oxidized and reduced state:
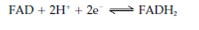
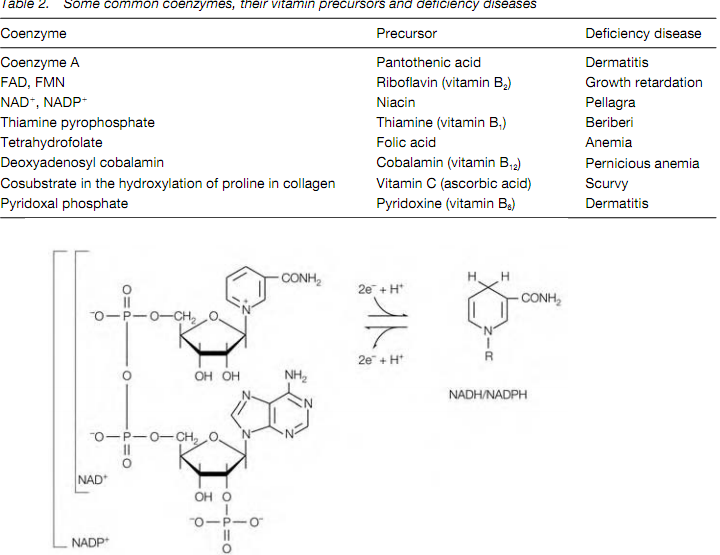
Figure: The structures of the coenzymes NAD+ and NADP+.