Operational Flow within Cad/Cam
In this section, the operational flow of functions essential to process an item through a manufacturing facility has been discussed in brief. These operation flows within the CAD/CAM environment have been illustrated by a flow chart. The box number in figure refers the sequence number.
1, 2. All planning should be the function of known customer orders & sales forecasts. If expected demand are not known/or estimated, the enterprise shall be working in a vacuum.
3. Management decisions based on expected orders leading to long-term order requirement that should be satisfied by either production or by subcontracting to outside sources (vendors).
4. A relatively low term evaluation of facility necessity is needed to plan which parts may be manufactured. For instance, enough machines of known capacity available, shall material be available, may we perform our needs with the current workforce etc. The aggregate planning function determines what product quantities must be produced in what time periods to satisfy the long-term requirements. The result of this activity is called as the master production schedule or master schedule. It is a schedule for final product, not for the components that go into the final product.
5. The master schedule is affected by current status conditions, so feedback loops come from many sources-including problems that might occur with deliveries from vendors, trouble in the shop floor, analysis that reveals demands cannot be satisfied because of to capacity problems, lack of vendors, etc.
6. The material requirements planning (MRP) function takes into consideration the current inventory levels for all of the components required to make the final products (a plant may have 20,000 part numbers and possibly 100 final products for which master schedules have been determined) as well as the components' bills-of-materials & lead time information (obtained from design & process planning data) and evolves component master schedules for all of components according to the demand requirements agreed upon.
MRP does not take into account whether manufacturing has adequate capacity to handle the job releases; therefore capacity planning (6a) evaluates shop loading in terms of the needs and feedback to the master schedule for corrective actions if any problems take place. A further function of MRP depend on such analysis is determining whether components must be produced in-house (6b) or subcontracted to outside vendors (6c).
7. Computer aided design is the function that should be completed after a demand for a product has been determined. Therefore, the sequence in which it is discussed in this section is not the similar as that of sequence or cycle starting from customer to inception through design, manufacturing, assembly & testing, and back to the customer. The design engineer may not talk in the same terms as the manufacturing engineer. For instance, lines, splines, circles, and arcs come under geometrical design while pockets chamfer, holes and so on come under manufacturing design. Process planning function is to accomplish the language transition from design to manufacturing.
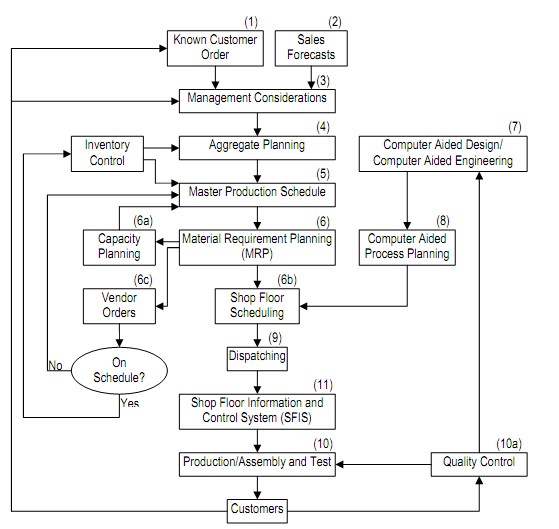
Figure : Flow of Operations in CIM
8. Some functions carried out by process planning modules are as :
- Sequence of operations required to manufacture a part
- Assessing the time requirement to complete the operations.
- Determining the type of machines and tooling required.
- Enumerate tolerance stacking problems that are credited because of multiple cuts/multiple components related to a part type.
The profitability & non-profitability of a part being manufactured might be ensured by the process planning function because it takes into account the various ways in which a part being manufactured. In order to obtain a detailed schedule, the information associated to process planning is fed into MRP analysis and also in the shop floor scheduling (6b). This step might result in the production of a detailed schedule for machines, tooling, fixtures, people and material handling devices, etc. To ignore the damage, all these have to come together at the right time.
9. Dispatching is the function of releasing all necessary items needed to perform an operation on a part so that part production should be completed within the schedule time.
10. Production & assembly is accomplished through local control computers and /or programmable controllers.
11. Finally, shop floor information system is responsible for getting the needed information passed to the downstream entities such like processing, local controllers and sequencing controllers, etc. In this way, real time status records are captured from the several equipments, machines and parts to activate feedback tools so like to ensure the correction or normal continuation of operations in the desired manner.