Voltage Divider
Very frequently, it is helpful to think of a series circuit as the voltage divider. The fundamental idea behind the voltage divider is to allocate a part of the total voltage to each resistor. In Figure (a) shown below, assume that the source voltage is E. By the circuit configuration illustrated one can divide off any voltage preferred (Vout), less than the supply voltage out E, by adjusting R1, R2 and R3.
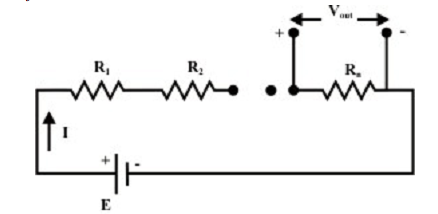
Figure (a): Voltage divider
From the figure (a) above the output of the voltage divider Vout is calculated by the relation shown below,

The above equation points out that the voltage across any resistor Ri (Ri I = 1, 2,….n ) in a series circuit is equivalent to the applied voltage ( E ) across the circuit multiplied by a factor
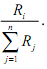
It must be noted that this expression is only valid when the same current I flows via all the resistors. When a load resistor is linked to the voltage divider (as shown in figure (b)), one can easily alter the expression above by simply combining RL and Rn in parallel to find a new 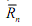 and substituting Rn by
and substituting Rn by 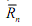
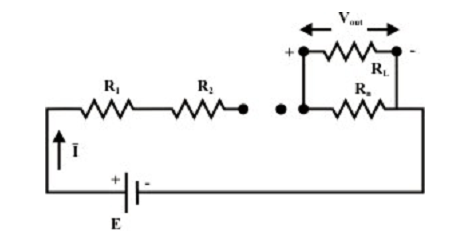
Figure: Voltage divider with load