Hydrogen bonding:
Hydrogen bonding can occur while molecules have a hydrogen atom attached to a heteroatom like nitrogen or oxygen. The common functional groups that can take part in hydrogen bonding are phenols, carboxylic acids, alcohols, amides, and amines. Hydrogen bonding is possible because of the polar nature of the N-H or O-H bond. Nitrogen and oxygen are much more electronegative than hydrogen. The result of it is, the heteroatom gains a little negative charge and the hydrogen gains a little positive charge. Hydrogen bonding includes the partially charged hydrogen of one molecule (the H bond donor) interacting with the heteroatom of other molecule (the H bond acceptor) that is partially charged.
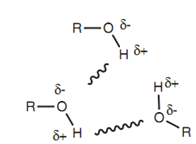
Figure: Intermolecular hydrogen bonding between alcohols.