Dipole-dipole interactions:
Dipole-dipole interactions are probable among polarized bonds other than N-H or O-H bonds. The very much likely functional groups that can interact in this way are those consisting of a carbonyl group (C = O). In the carbonyl bond the electrons are polarized towards the more electronegative oxygen like that the oxygen gains a minor negative charge and the carbon gains a minor positive charge. This causes in a dipole moment that can be presented via the arrow displayed in below diagram. The arrow in the diagram points to the negative end of the dipole moment. Molecules consisting of dipole moments can align themselves with each other like that the dipole moments are pointing in opposite directions.
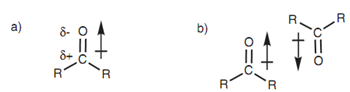
Figure: (a) Dipole moment of a ketone; (b) intermolecular dipole-dipole interaction between ketones.