Transition between energy levels:
The transitions amongst these energy states might be brought about through absorption of a photon of suitable energy or these might lead to release of such a photon. In easy words we could say that the system may absorb energy and go from the lower energy state (ground state), E1, to higher energy state (excited state), E2 by absorbing a photon of energy equal to the difference of the energies of the two states i.e.,
?E = E2 - E1 = hν
where, h is the Planck's constant and has the value of 6.626 × 10-34 J s (joules second) ν is the frequency of electromagnetic radiation which is causing the energy changes. Alternatively, a system initially in the higher energy state E2 can go to the lower energy state E1 by emitting a photon of the energy equal to the difference in energies. The energy changes can be shown as in Figure. As you can see here in ?E is the energy change associated with the transition between the energy levels E1 and E2.
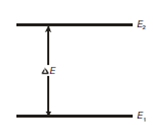
Figure: Diagram showing energy change during transition between energy levels
Yet another possibility is of the radiation getting scattered. The three phenomena occurring due to interaction of radiation with matter viz. absorption, emission and scattering are explained in the following subsections.