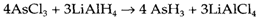Exchange and metathesis reactions
The simple most type of exchange reaction might be written AB+C→AC+B and is exemplified by
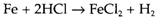
In this case the direct combination of chlorine and iron gives FeCl3, demonstrating that exchange reactions may give a distinct results compared with direct combination. The reaction AB+C→AC+B can also be helpful for preparing the element B, several of the extraction methods for elements discussed in the Topic B4 being of this type. One issue for preferring exchange to direct combination is that one of the elements might not be simple to work with. Even though fluorine combines directly with nearly every element, it is a unpleasant and dangerous an gas, and is frequently replaced by a fluorinating agent like ClF3 in laboratory and industrial processes:
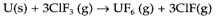
The more difficult exchange process AB+CD→AD+CB is explained as substitution or metathesis. An instance also involving fluorination is
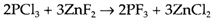
that is employed to make PF3 as direct combination of P with fluorine gives the pentafluoride PF5. Metathesis reactions are general in the preparation of organic derivatives of elements, by using the organo-lithium or -magnesium (Grignard) reagents produced by direct synthesis:
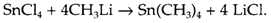
They are particularly valuable for making compounds that are not thermodynamically stable according to their constituents, and so cannot be made by direct reaction. For instance, thermodynamically unstable hydrides may be made by using LiAlH4 or NaBH4: