Direct combination and decomposition reactions
Inorganic substances' reactions and the techniques used in the synthesis process of compounds are very different. This segment summarizes some of the chief reaction types and their applications. The simple most type of reaction is the direct combination of two elements to form a binary compound, A+B→AB. For instance
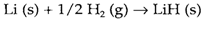
Several binary compounds, particularly oxides and halides of elements, might be made in this direct way, even though there are limitations. It is understandable that the formation of the desired compound AB must be thermodynamically favourable. There may also be kinetic difficulties and the above synthesis of LiH needs a temperature of 600°C for conquer the activation energy related with breaking the H-H bond. The reaction may be facilitated by using a catalyst, in some cases like in the synthesis of ammonia from H2 and N2.
The scope of direct combination reactions is very expanded if one or more of the species A and B is a polyatomic group rather than an element. An instance also involving lithium is
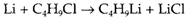
In the example of thermodynamic stability of LiCl aids the formation of the required result butyl lithium (C4H9Li), that is a useful reagent for making alkyl derivatives of other elements.
The opposite of combination is decomposition, AB→A+B. The mercury oxide's thermal decomposition,
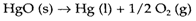
was historically significant in the discovery of oxygen but simple reactions of this kind are seldom useful in practice, even though the decomposition of compounds by electrolysis is significant in the production of some elements. More complex thermal decomposition reactions like
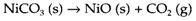
may be helpful in the preparation of compounds (NiO in this instance) that are hard to make in pure and stoichiometric form by direct combination. Several oxo-salts (carbonates, nitrates, etc.) and hydroxides of metallic elements decompose in a identical way to oxides on heating. The temperatures needed to get these endothermic reactions can frequently be correlated with the size and charge of the metal ion.