NITROGEN
The element
Nitrogen is a fairly electronegative element but the huge strength of the triple bond creates N2 thermodynamically and kinetically stable. The atom can create three single bonds, generally with a pyramidal geometry, but also has a remarkable tendency to multiple bonding. Its uncommonly rich redox chemistry is demonstrated in the Frost diagram in Fig. 1 (see below). Dinitrogen creates 79 mol % of dry air. The element is important for life and is one of the elements frequently in short supply, as fixation of atmospheric nitrogen to create chemically use ful compounds is a hard process. Nitrogen is get from the atmosphere by liquefaction and fractional distillation. Its usual boiling point (77 K or -196°C) and its ready accessibility make it a helpful coolant. It directly reacts with rather few elements and is frequently used like an inert filling or 'blanket' for metallurgical processes. The majority of industrial nitrogen, though, is used to make ammonia and more compounds.
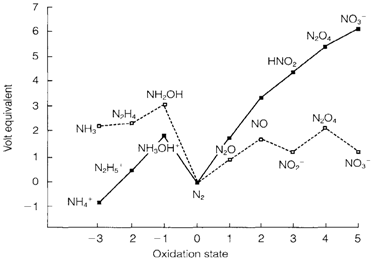
Fig. 1. Frost diagram showing the redox states of nitrogen in water at pH=0 (continuous line) and pH=14 (dashed line).