Many-Electron Atoms
The helium atom is a good instance of a many-electron atom (i.e. an atom which consists of more than one electron). Fundamentally no new problems are encountered whether we refer two or ten electrons, but a very significant problem encounters in passing from the one-electron to the two-electron case. To notice what this problem is, refer all the potential interactions found in a helium atom. Once more, consider the electrons to be point charges and "freeze" them at some immediate positions in space.
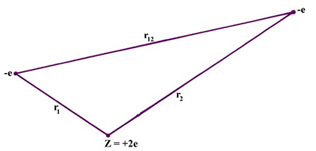
Fig. The potential interactions in an He atom. The electrons are entitled by their charge -e, and the nucleus by its charge Z = +2e.
The potential energy, the average value of that is to be determined by quantum mechanics, is
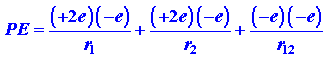
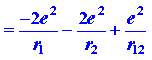
The first and second terms in equation (1) denote the attraction of the helium nucleus (for which Z = 2) for electrons 1 and 2 correspondingly. The last term denote the repulsion between the two electrons. It is this last term that makes the problem of the helium atom and of all many-electron atoms, hard to solve. No direct solution to the problem present, the reason being that there are so many interactions to consider concurrently. We must make some estimation in our approach to this problem.