Ligand field theory
Ligand field theory (LFT) explains the bonding, orbital arrangement, and another features of coordination complexes. It demonstrates an application of molecular orbital theory to transition metal complexes.
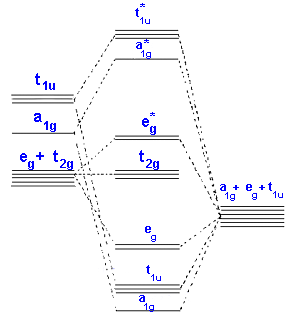
A transition metal ion comprise nine valence atomic orbitals, five (n)d, one (n+1)s, and three (n+1)p orbitals. These orbitals are of suitable energy to create bonding interaction along with ligands. The LFT analysis is extremely dependent on the geometry of the complex, but most description begin through describing octahedral complexes, in which six ligands coordinate to the metal.