BRONSTED ACIDS AND BASES
Definitions
A Bronsted base a proton acceptor, and a Bronsted acid is a proton donor. According to this definition an acid-base reaction includes protolysis:
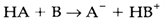
HA is termed as the conjugate acid to A-, and A- the conjugate base to HA; HB+ and B creat other conjugate acid-base pair. Instances of some conjugate pairs (with the acid given first) are:
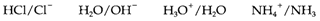
The Water is both an acid and a base and this also occurs with polyprotic (or polybasic) acids like H2SO4, which can go through successive protolysis steps to give HSO4-and SO2- so HSO4- is the conjugate base of H2SO4 however the conjugate acid of SO2-4.
This definition of acids and bases should not be get puzzled with the Lewis definition even though there is a connection: H+ is a Lewis acid and Bronsted bases are also Lewis bases, but generally Lewis acids like BF3 are not Bronsted acids, and Bronsted acids like HCl are not Lewis acids. Bronsted acidity is dependent on solvent. Substances like HCl are covalent molecules that go through protolysis only in solvents polar sufficient to solvate ions, and when a base is exist (which may be a solvent molecule). Basi concentration of this discussion is on water, the most common solvent in which protolytic reactions are studied.