BINARY COMPOUNDS: FACTORS INFLUENCING STRUCTURE
A binary compound is a chemical compound that consists of exactly two distinct elements. Instances of binary ionic compounds involve calcium chloride (CaCl2), andmagnesium oxide (MgO), sodium fluoride (NaF), whilst instances of binary covalent compounds involve water (H2O), carbon monoxide (CO), and sulfur hexafluoride (SF6).
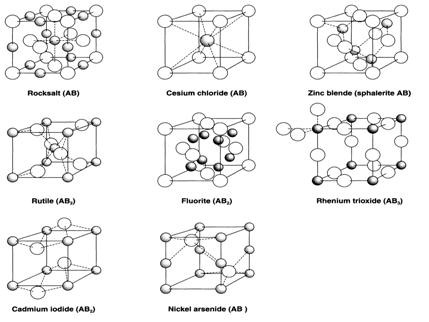
A relative analysis of binary compounds and 61 simple anhydrous salts M(y)(LO(3))(z) (L = S, Se, Te, Cl, Br, I) was performed by using the crystallochemical program package TOPOS. A topological resemblance was found among the salts and six types of binary compounds (NaCl, NiAs, PoCl(2), Tl(2)S(2), ZnTe, rutile). It is noticeable that these structure relationships are usual for other groups of inorganic salts: carbonates, borates, nitrates, orthophosphates, selenates, perchlorates, molybdates, orthoarsenates, sulfates,and halogenides of d-metals. For every the M(y)(LO(3))(z) compounds the uniformity and topology of the ion arrays were examined. It has been recognized that in 36 out of the 61 salts minimum one ion array has the topology of close packing or the body-centred cubic lattice. The results obtained have permitted us to come to conclusions about the structure-forming role of the arrays of several chemical composition.