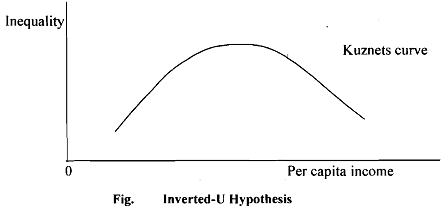
Inverted-U Hypothesis:
It was argued by Simon Kuznets (1955) that a country's industrialization process in he initial phases could lead to higher income inequalities. The process gets reversed as the level of industrialization goes up. Kuznets gave empirical examples from developed countries to prove his argument. He hypothesized that the relationship between the level of economic development and income inequality takes the form of an inverted U-curve. This hypothesis is commonly referred to as the inverted-U hypothesis and the curve is called the Kuznets' curve. In particular, Kuznets postulated that the itersectoral shifts which occur in,the early stages of economic development accentuate inequality. However, after reaching certain threshold level of development, inequality attains its peak and then declines in later stages. The Kuznets curve is based on empirical findings. Usually Gini coeffecient is taken as the measure of inequality. When Gini coefficient. it is plotted against a quadratic function of per capita income we obtain the Kuzets curve. In Fig. we show a hypothettical Kuznets' curve. The possible reason behind Kuznets curve is that in early stages of development, when investment in physical capital is the main engine of economic growth, inequality spurs growth by directing resources towards those who save and invest the most. In more mature economies, on the other hand, human capital accumulation takes the place of physical capital accumulation as the main source of growth. Moreover, inequality impedes growth by hurting education because poor people cannot fully finance their education.
The Kuznets' curve is extended to other areas including environment. The environmental Kuznets curve is a hypothesized relationship between various indicators of environmental degradation and income per capita. In the early stages of economic growth there is an increase in environmental degradation and pollution, but beyond some level of income per capita (which will vary for different indicators) the trend reverses. Consequently, at high-income levels economic growth leads to environmental imprc~vement and there is decline in the level of environmental degradation. This implies that the e~ivironmental impact on an indicator is an inverted U-shaped function of income per capita. Typically the logarithm of the indicator is modeled as a quadratic function of the logarithm of income.
Many studies have shown the implications of inverted-U hypothesis. First, high income inequality may increase absolute poverty which may, in turn, adversely affect the quality of health, education, nutrition, etc. resulting in poor quality of human capital. Second, rising inequality in favor of a small minority of the population may heighten social and political tension and threaten a country's long- run development prospects. With the interaction of economic and political forces, policy makers may not formulate correct policies to enable long term income redistribution.