Nmr spectrum of methyl ethanoate:
In the next case we have a methyl group that is next to a ketone group. A ketone group has an electron withdrawing effect that reduces the electron density around the neighboring methyl group (deshielding), and thus the chemical shift is higher at approximately 2.2 ppm.
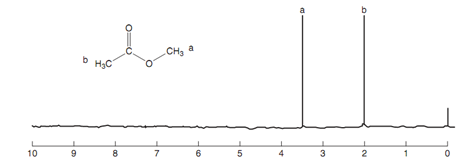
Figure: Nmr spectrum of methyl ethanoate
Electron withdrawing effect of an oxygen atom or positively charged nitrogen is much greater still and thus a methyl ether group has a signal at about 3.3 ppm, identical to the methyl signal of a quaternary ammonium salt.
Because the position of a signal in the nmr spectrum is associated to inductive effects, it is probable to use this knowledge to assign dissimilar signals in an nmr spectrum. For instance, the nmr spectrum for methyl ethanoate consists of two signals at 2.0 and 3.5 ppm. The signal at 3.5 ppm can be assigned to CH3a because it is directly attached to oxygen. The oxygen has a stronger electron withdrawing effect as compared to the carbonyl group. NMR tables are as well available which depict the typical chemical shifts for specific groups.