Parallel Opposing:
Figure illustrates two coils coupled in parallel where the mutually induced e.m.f in a coil because of change in current in the other coil is negative.
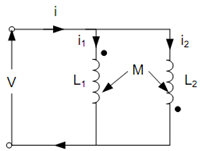
Figure: Inductive Coupling in Parallel (Flux Opposing)
Using Kirchoff's voltage law, we can write
V = L1 (di1/dt) - M (di2/ dt)
Also,
V = L2 (di2/dt) - M (di1/ dt)
From Eqs. (53) and (54), we get
L ( di1 /dt) - M di2 /dt = L2 (di2/dt) - M (di1/ dt) ---- (60)
Now
i = i1 + i2
i2 = i - i1
Substituting i2 from Eq. (56) in Eq. (55), we obtain
L di1/dt - M d (i - i1 )/dt = L2 + d (i - i1 ) - M(di1/dt)
L di1/dt - M d i /dt + M d i /dt = L2 + di /dt - M(di1/dt)
(L1 + L2 + 2M ) di1/dt = (L2 + M ) di1/dt
∴ di1 /dt = ( (L2 + M )/(L1 + L2 + 2M) (di /dt )
Likewise, di2 /dt = (L1+M/ L1 + L2 + 2M ) di/dt
Using Eqs. (57) and (58) in Eq. (53), we obtain
V = L1 (L2 + M/ L1 + L2 +2M) di/dt + M(L1 + M ) / (L1 + L2 + 2M ) (di/dt)
or, V = (L1 L2 + L 1M + L1 M - M 2) / (L1 + L2 +2M) di/dt
or V = (L1 L2 - M2 )/ (L1 + L2 + 2M) di/dt
Let L be the equivalent inductance of the parallel combination, then we can write
V = L (di /dt)
From Eqs. (61) and (62), we obtain
L (di/dt ) = (L1 L2 - M2 )/ (L1 + L2 + 2M) di/dt
L = (L1 L2 - M2)/ (L1 + L2 +2M)