Constructional Details:
An induction motor contains two main parts, i.e. stator and rotor. An induction motor contains the same physical stator as a synchronous machine. Both stator and rotor are cylindrical. The magnetic flux is generated by the stationary winding housed in the outer part, the stator, to which the supply is connected while the inner part, the rotor, which is also called armature, carries rotor winding in which the current is induced.
Stator
The stator core is built up of laminations which can or cannot be insulated by varnish. Thicker laminations are utilized in small motors. A partially wound stator of induction motor is illustrated in Figure
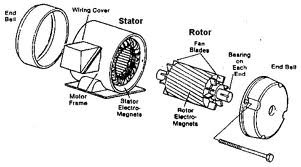
Figure: A Partially Wound Stator of Induction Motor
The stator of poly phase induction motor carries the poly phase AC windings. Stator winding is totally insulated as per the voltage ratings. Generally we shall use the double layer winding owing to the ease of manufacture, assembly and repair.
There are two different kinds of induction motor rotors which may be placed inside the stator. One is called squirrel cage rotor or simply a cage rotor, whereas the outer is called a wound rotor. Figure (a) illustrates squirrel-cage induction motor rotor and Figure shows wound rotor of poly phase induction motor.
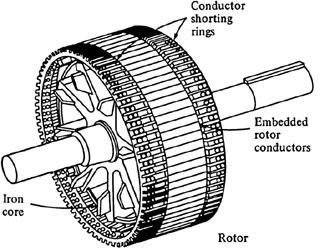
Figure: Sketch of Squirrel-cage Rotor