Air Gap Power, Torque and Output Power:
As illustrated in Figure, the power crossing the terminals 1-2 is the electrical power input per phase minus the stator copper loss and iron loss. It is the power transferred from the stator to the rotor via the air gap magnetic field. The PG is the three-phase value and known as air gap power.
It is apparent from the equivalent circuit that
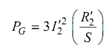
Power across air gap = Rotor copper loss /Slip
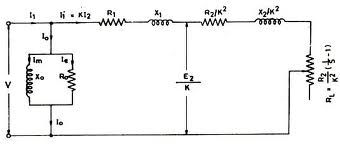
Figure: Equivalent Circuit of Induction Motor
Therefore mechanical power output (Gross)
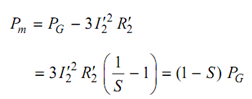
Rotor speed is
ωr = (1 - S ) ωs rad (mech)/sec
Then the electromagnetic torque developed is given by
(1 - S ) ωs Te = Pm = (1 - S ) PG
or
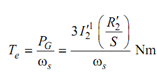
The net mechanical power output and torque are attain by subtracting losses-windage, friction and stray load loss.