Indifference Curve:
An indifference curve joins together all points representing different combinations of two goods which yield the same utility. It is defined as locus of various combinations of two commodities.
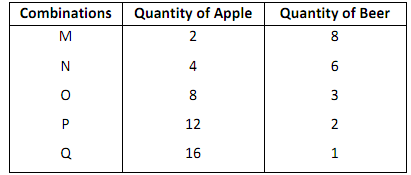
Figure illustrates an indifference curve for the data in Table 4.4
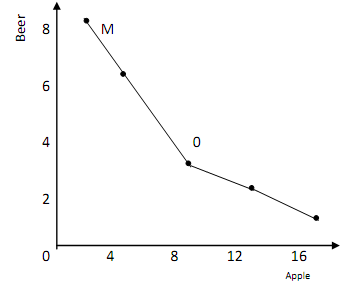
The idea here is that all the combinations labelled M to Q are ranked equal in terms of satisfaction derived by the consumer and, he has no reason to prefer one to the other.
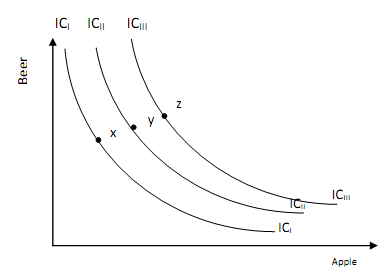
A set of indifference curves showing different levels of utility is called an indifference map (see Figure 4.7), the farther away from the origin, the higher the level of utility being illustrated.
It follows from figure , that a rational consumer will prefer combination Y to X, and Z to Y.