Vector representation of impedance:
Any impedance R+ jX is represented by a complex number of form a+ jb. Let R = a and X = b.
It must be easy to visualize, now, how impedance vector changes as either R or X, or both can be varied. If X remains constant, an increase in the value R will cause the vector to get longer. If R is constant and XL gets larger, the vector will grow longer. If R remains the same as XC gets larger, the vector will grow longer again. Think of point a+ jb, or R+ jX, moving around in plane, and imagine where the corresponding points on axes lie. These points are found by drawing dotted lines from point R+ jX to R and X axes, such that the lines intersect the axes at right angles.
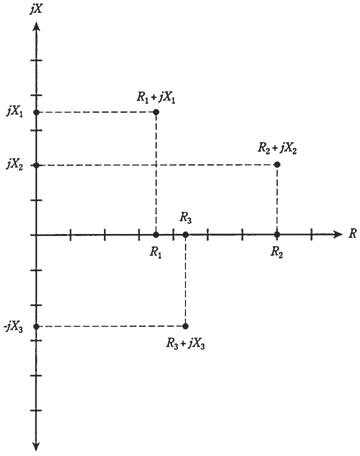
Figure-- Some points in the RX plane, and their components on R and X axes.
Now think of points for R and X moving toward right and left, or up and down, on the axes. Assume that what happens to the point R+ jX in the various scenarios. This is how the impedance changes as resistance and reactance in the circuit are varied.
Resistance is 1-dimensional. Reactance is 1-dimensional. But impedance is 2-dimensional. To fully define impedance, you should render it on the half plane, specifying the resistance and reactance, which are independent.