Oblique Central Impact:
Figure illustrates two spherical masses m1 and m2 whose initial velocities V1 and V2 are not collinear. It is supposed that impulsive forces act normal to the surfaces of contact. For purpose of convenience, the common tangent at the point of contact of the two spherical masses is supposed along x axis as shown in the figure.
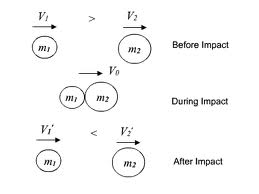
Therefore the line joining centres of the two spheres represents y axis. In such a case of
Oblique-Impact V1, V2, θ1 and θ2 are given and four unknowns are:
a. Final velocities - (V1′ and V2′) , and
b. Their directions - (θ1′ and θ′2 )
Let V1 x , V2 x , V1x ', V2x' be the components of velocities in the x direction. Let V1 y , V2 y , (V1y )' , (V2y)' be components of velocities in y direction. We may now consider two vector equations along x and y directions for the principle of conservation of momentum.
∴ m1 V1 x + m2 V2 x = m1 (V1x)' + m2 (V2x)'
And ∴ m1 V1y + m2 V2y = m1 (V1y)' + m2 (V2 y)'
Figure 8.20
Since the impulsive forces may act only in y direction normal to the surface of contact, we have
∴( V2y )' - (V2 y )' = e (V1y - V2y )
Since impulsive forces in x direction are not developed the component of velocities in X direction is not altered.
∴ (V1x )' = V1x
(V2x )' = V2x