Imaginary Numbers:
Imaginary numbers give output while a mathematical operation yields the square root of a negative number. For instance, in solving the quadratic equation x2 + 25 = 0, the solution yields x2 = -25. Therefore, the roots of the equation are x = ± √-25 The square root of (-25) is known as an imaginary number. In fact, any even root (that is square root, 4th root, 6th root, etc.) of a negative number is known as an imaginary number. All other numbers are known as real numbers. The name "imaginary" may be somewhat misleading since imaginary numbers actually exist and can be used in mathematical operations. They could be added, subtracted, divided & multiplied.
Imaginary numbers are written in a form various from real numbers. Because they are radicals, they can be simplified through factoring. Therefore, the imaginary number √-25 equals 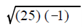 that equals 5√-1. Similarly, √-9 equals
that equals 5√-1. Similarly, √-9 equals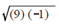 , that equals 3√-1 . All imaginary numbers can be simplified in that way. They can be written as the product of a real number and √-1. In order to additional simplify writing imaginary numbers, the imaginary unit i is described as √-1. Therefore, the imaginary number,√-25, that equals 5√-1, is written as 5i, and the imaginary number, √-9 , which equals 3√-1, is written 3i. By using imaginary numbers in electricity, the imaginary unit is frequent represented by j, on the other hand of i, since i is the common notation for electrical current.
, that equals 3√-1 . All imaginary numbers can be simplified in that way. They can be written as the product of a real number and √-1. In order to additional simplify writing imaginary numbers, the imaginary unit i is described as √-1. Therefore, the imaginary number,√-25, that equals 5√-1, is written as 5i, and the imaginary number, √-9 , which equals 3√-1, is written 3i. By using imaginary numbers in electricity, the imaginary unit is frequent represented by j, on the other hand of i, since i is the common notation for electrical current.
Imaginary numbers are added or subtracted through writing them using the imaginary unit i and then adding or subtracting the real number coefficients of i. They are added or subtracted such as algebraic terms in that the imaginary unit i is treated like a literal number. Thus, √-25 and √-9 are added by writing them as 5i and 3i and adding them like algebraic terms. The output is 8i which equals 8√-1 or √ -64. Same, √-9 subtracted from √-25 equals 3i subtracted from 5i that equals 2i or 2√-1or√-4.