Modes:
An electroactive substance undergoing electrode reactions at micro electrode is brought to the electrode by three modes:
i) Migration of charged ions under the influence of an electric field due to attraction of the electrode that has a positive or negative charge.
ii) Convection resulting from stirring or vibration.
iii) Diffusion because of concentration gradient established near electrode during the reaction.
This is the current in which is proportional to the concentration of electroactive substance and is given by
il = (nFAD/ δ) ca
where
ca = Concentration of analyte, n = number of electrons, F = Faraday constant,
A = Area of the electrode surface, D = Diffusion coefficient of the analyte,
il = Limiting current, δ = thickness of Nernst layer
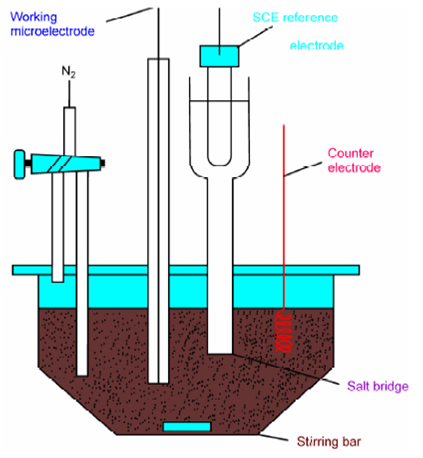
Figure: A three electrode cell for hydrodynamic voltammetry