Cyanide addition:
Nucleophilic addition of a cyanide ion to an aldehyde or ketone provides a cyanohydrin. In this reaction, there is a catalytic amount of potassium cyanide available and this supplies the attacking nucleophile in the type of the cyanide ion (CN-).
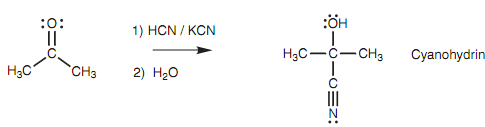
Figure: Synthesis of a cyanohydrin.
The nitrile group's nucleophilic center is the carbon atom because this is the atom with the negative charge. The carbon atom employs its lone pair of electrons to create a new bond to the electrophilic carbon of the carbonyl group as shown in figure. Since this new bond creates, the comparatively weak π bond of the carbonyl group breaks and the two electrons creating that bond move onto the oxygen to provide it a third lone pair of electrons and a negative charge.