Carbonyl groups
Similar theory describes the bonding in a carbonyl group (C=O) in which both the carbon and oxygen atoms are sp2 hybridized. The subsequent energy level diagram displays how the valence electrons of oxygen are set after sp2 hybridization. Two of the sp2 hybridized orbitals are filled along with lone pairs of electrons that leave two half-filled orbitals obtainable for bonding. The sp2 orbital can be employed to create a strong σ bond, whereas the 2py orbital can be employed for the weaker π bond. Figure displays how the σ and π bonds are created in the carbonyl group and describes why carbonyl groups are planar with the carbon atom comprising a trigonal planar shape. It also describes the reactivity of carbonyl groups because the π bond is weaker as compared to the σ bond and is more likely to be included in reactions.
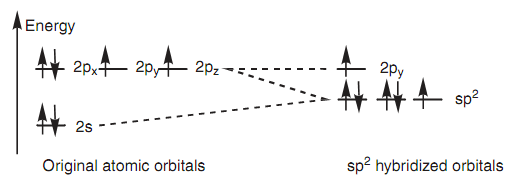
Figure: Energy level diagram for sp2 hybridized oxygen.
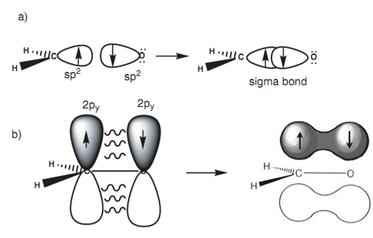
Figure: (a) Formation of the carbonyl σ bond; (b) formation of the carbonyl π bond.