Design Evaluation
At Once an operational user interface prototype has been building it must be evaluated to determine whether it meets the requirement of the user. The Evaluation can span a formality spectrum which ranges from an informal test drive in that a user gives impromptu feedback to a formally designed study which uses statistical techniques for the evaluation of questionnaires completed through a population of end users.
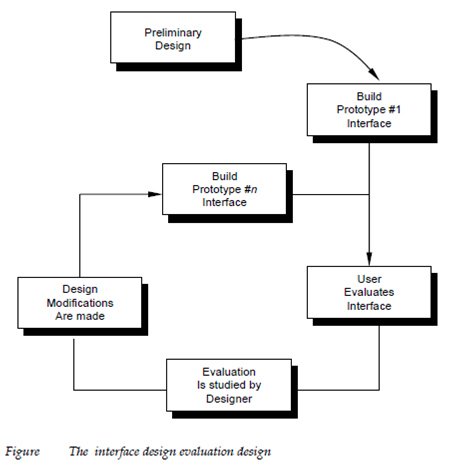
The user interface evaluation cycle takes the form which is described in Figure 22.3. After the preliminary design has been finished a 1st level prototype is build. The prototype is evaluated through the user who gives the designer with direct comments about the efficacy of the interface. Additionally if formal evaluation methods are used for example questionnaires rating sheets the designer may extract information from this information example for 80 % of all users did not like the mechanism for saving data files. The Design modification is made based on user input and the next level prototype is established. The evaluation cycle continues until no future modifications to the interface design are necessary but is it possible to evaluate the quality of a user interface behind a prototype is establish? If potential problems can be uncovered and corrected previously the number of loops by the evaluation cycle will be development and reduced time will shorten.
When a design model of the interface has been established a number of evaluation criteria can be applied during before time design reviews are:
1. Complexity and The length of the written specification of the system and its interface give an indication of the amount of learning needs through users of the system.
2. The number of actions or commands specified and the average number of arguments per command or individual operations per action gives an indication of interaction time and the overall efficiency of the system.
3. The number of actions system and commands states indicated byte design model indicate the memory load on users of the system.
4. Interface style help error handling and facilities protocols give a general indication of the complexity of the interface and the degree to that will be accepted through the user.
Once the 1st prototype is establish the designer can collect a variety of quantitative and qualitative data which will assist in evaluating the interface. By collect qualitative data questionnaires can be distributed to user of the prototype can be (1) simple yes or no (2) numeric (3) scaled subjective (4) %percentage subjective. Examples are:
1.Were the commands simple to remember?
2.How many various commands did you use?
3.How simple was it to learn basic system operations?
4.Compared to other interfaces you have used, how would this rate? Top 25 percent, Top 1 percent, top10 percent, top 50 percent, bottom 50 percent
If qualitative data are preferred a form of time study analysis can be conducted. Users are observed in the duration of interaction and data like as number of tasks right completed over a standard time frequency of command use ,time period, sequence of commands time spent looking at the display, number of errors category of error and error recovery time which time spent using help and number of help references per standard time period are collected and used as a guide for interface modification.