Glycolysis and alternative pathways
The reactions termed glycolysis (Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas) take place in the cytoplasm of many prokaryotes and eukaryotes. This is well described in many biochemical textbooks including Instant Notes in Biochemistry.
Some important groups of Bacteria for example some Gram-negative rods do not use glycolysis to oxidize glucose. They use a different mechanism, the Entner-Doudoroff pathway in Figure 1, which yields one mole of ATP, NADPH and NADH from every mole of glucose. This is a hexose monophosphate pathway HMP and in this pathway only one molecule of ATP is produced per molecule of glucose metabolized.Another HMP is the phosphoketolase pathway which is another technique for glucose breakdown found in Lactobacillus and Leuconostoc spp. When grown on five-carbon sugars (pentoses). The pathway produces lactic acid, CO2 and either ethanol or acetate in Figure 2.
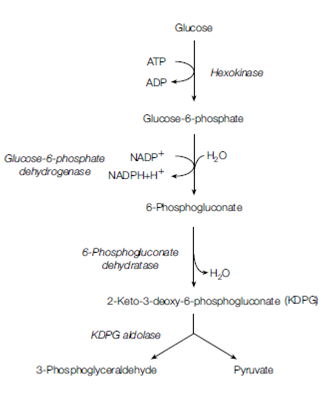
Figure 1. Entner-Doudoroff pathway.
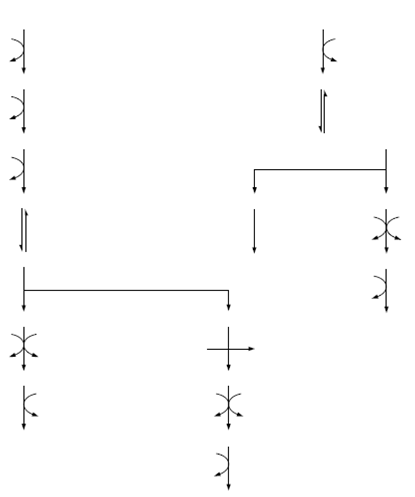
Figure 2. The phosphoketolase pathway.
An important HMP is the pentose phosphate pathway PPP which often operates in conjunction with glycolysis or other HMP pathways. PPP is an important provider of intermediates that serve as substrates for other biosynthetic pathways. This pathway yields NADPH + H+ and pentoses which are used in the synthesis of nucleotides including FAD, ATP, and coenzyme A (CoA).
The reactions can be summarized as:
Glucose-6-phosphate + 2 NADP+ + water --> ribose-5-phosphate + 2 NADPH + 2H+ + CO2
There are three important stages to this pathway.
1. Glucose-6-phosphate is converted to ribulose-5-phosphate, generating two NADPH+ 2H+.
2. Ribulose-5-phosphate isomerizes to ribose-5-phosphate.
3. Excess ribose-5-phosphate is converted to fructose-6-phosphate and glyceraldehyde via a series of reactions to enter glycolysis.
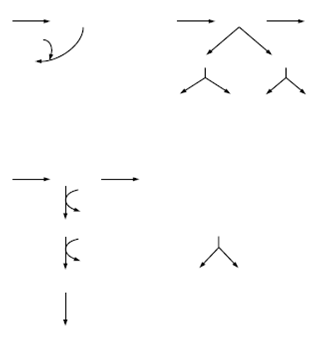
Figure 3. Products of fermentation. (a) Mixed acid. (b) Butanediol.