Comparison of the Types of Heat Exchangers:
Every of the three categories of heat exchangers have benefits and drawback. But of the three, the counter flow heat exchanger design is the most efficient while contrast heat transfer rate per unit surface area. An effectiveness of a counter flow heat exchanger is because of the fact in which the average ?T (difference in temperature) among the two fluids over the length of the heat exchanger is maximized, as display in Figure. Thus the log mean temperature for a counter flow heat exchanger is larger than the log mean temperature for a same parallel or cross flow heat exchanger. (Also See the Heat Transfer, Thermodynamics, and Fluid Flow Fundamentals Handbook for a review of log mean temperature). This could be seen through comparing the graphs in Figures. The subsequent exercise elaborates how the higher log mean temperature of the counter flow heat exchanger results in a larger heat transfer rate. A log mean temperature for a heat exchanger is calculated by using the subsequent equation.
?Tlm = ?T2 - ?T1/ln(?T2/?T1) (2-1)
Heat transfer within a heat exchanger is through convection and conduction. A rate of heat transfer, "Q", in a heat exchanger is calculated by using the following equation.
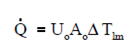 (2-2)
(2-2)
Where:
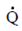 = Heat transfer rate (BTU/hr)
= Heat transfer rate (BTU/hr)
Uo = Overall heat transfer coefficient (BTU/hr-ft2-°F)
Ao = Cross sectional heat transfer area (ft2)
DTlm = Log mean temperature difference (°F)
Let assume the following instance of a heat exchanger operated under identical conditions as a counter flow and after that a parallel flow heat exchanger.
T1 = represents the hot fluid temperature
T1in = 200°F
T1out = 145°F
Uo = 70 BTU/hr-ft2-°F
Ao = 75ft2
T2 = represents the cold fluid temperature
T2in = 80°F
T2out = 120°F
Counter flow ?Tlm = (200-120oF) - (145 - 80oF)/ln ((200- 120oF)/ (145- 80oF)) = 72oF
Parallel flow ?Tlm = (200- 80oF) - (145- 120oF)/ln ((200- 80oF)/ (145- 120oF)) = 61oF
Inserting the above values within heat transfer Equation (2-2) for the counter flow heat exchanger yields the subsequent output.
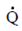 = (70 (BTU/hr- ft2- oF))(75ft2) (72oF)
= (70 (BTU/hr- ft2- oF))(75ft2) (72oF)
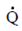 =3.8x105 (BTU/hr)
=3.8x105 (BTU/hr)
Inserting the above values into the heat transfer Equation (2-2) for parallel flow heat exchanger yields the following result.
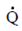 = (70 (BTU/hr- ft2- oF))(75ft2) (61oF)
= (70 (BTU/hr- ft2- oF))(75ft2) (61oF)
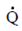 =3.2x105 (BTU/hr)
=3.2x105 (BTU/hr)
The results described along with given the similar operating conditions, operating the same heat exchanger in a counter flow manner will give output in a greater heat transfer rate than operating within parallel flow.