Mechanism:
Because acid conditions are used, this process does not include an enolate ion. In place of it, the reaction takes place by the enol tautomer of the carbonyl compound. The enol tautomer works like a nucleophile with a halogen by the mechanism displayed in figure. In the last step, the solvent works as a base to remove the proton.
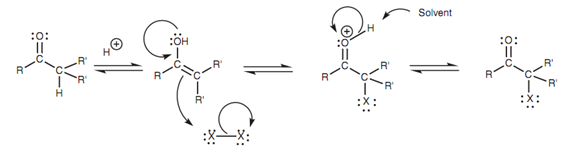
Figure: Mechanism of α-halogenation.