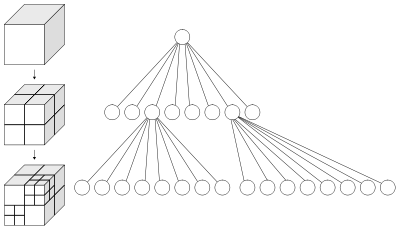
Octree Encoding:
Octress are hierarchical variant of spatial-occupancy enumeration, designed to address that approach's demanding storage needs. Octress are in turn derived from quadtrees, a 2D representation format utilized to encode images. The basic idea behind the quadtree and octree both is the divide-and-conquer power of binary subdivisions. A quadtree is derived by successively subdividing a 2D plane in both of the dimensions to form quadrants, as illustrated in Figures (a) and (b). While a quadtree is utilized to represent an area in the plane, each quadrant might be full, partially full, or empty; based on how much of the quadrant intersects the area. A partially full quadrant is recursively subdivided into sub quadrants. Subdivision continues until a predetermined cut off depth is attained. Whenever four sibling quadrants are full or empty uniformly, they are deleted and their partially full parent is replaced along a full or empty node. In octree encoding, they are deleted and their partially full parent is replaced along with a full or empty node. In octree encoding, we include the object to be modelled inside a cube. If the object does not cover uniformly the cube, then we subdivide the cube in eight octants. If any resulting octants is full (entirely inside the object) or empty (completely outside the object), no further subdivision is made. If any of the octants is partially full, we again subdivide it into octants. We continue to subdivide the partially full octants till the resulting octants are either full or empty or till some predetermined level of subdivision is attained.