Lower oxidation states
Gas-phase molecules like AlH, AlCl and AlO are well known at low pressures and high temperatures but, like in group 2, disproportionation takes place under normal circumstances due to the much higher lattice or solvation energies related with M3+. Like these energies get decrease with ion size down the group, the trend to disproportionation also declines, and lower oxidation states become common. Diagram 1 depicts the possibility of forming In+ and Tl+, the former prone to disproportionation, the later very much stable. The rising stability of ions with the (ns)2 configuration in lower periods is frequently called the inert-pair effect. It is mainly marked in period 6 due to the high ionization energies of these elements but it is significant to keep in mind that it relies not on ionization energies alone but on a balance of dissimilar energy trends.
Like K+, that has a very identical size, Tl+ is extremely basic in solution, and forms some compounds with identical structures to those of alkali metals (example TlCl has the CsCl structure). Though It has a larger affinity for soft ligands and sometimes solid structures of its depict an irregular coordination suggesting the affect of a lone-pair of electrons as with SnII.
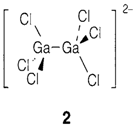
Ga and In create +1 compounds with large low-charged anions and also some where the oxidation state is actually +2 (or sometimes even fractional). The gas-phase M2+ ions comprise the (ns)1 configuration with one unpaired electron and in chemical situations all the time either disproportionate or create metal-metal bonds. The former probability leads to mixed valence compounds like 'GaCl2' (actually, Ga+[GaIIICl4]-). The option gives ions [M-M]4+ (isoelectronic to Hg2+2), even though they are never found on their own but are all the time strongly bonded to ligands, like in [Ga2Cl6]2- (2). (Note: the variation among this structure and that of Ga2Cl6 (like Al2Cl6), in which there are no electrons presented for direct Ga-Ga bonding.)
Every elements of the group create Zintl compounds with electropositive metals. Continuous networks of covalently bonded atoms are usually found, than the clusters common with group 14. For instance, NaAl and NaTl comprise the tetrahedral diamond-like networks of Al or Tl that can be understood on the basis that Al- and Tl- have similar valence electron count, like carbon.