Grains and Boundaries:
The grain boundary refers to the outside area of a grain that separates it from other grains. A grain boundary is a region of misfit among the grains and is commonly one to three atom diameters huge. The grain boundaries divided variously-oriented crystal regions (polycrystalline) in that the crystal structures are identical. Another figure represents four grains of various orientation and the grain boundaries which arise at the interfaces among the grains.
An extremely important characteristic of a metal is the average size of the grain. A size of the grain determines the properties of the metal. For instance, smaller grain size raises tensile strength and tends to increase ductility. The larger grain size is preferred for improved high-temperature creep properties. Creep is the permanent deformation which increases along with time under constant load or stress. A Creep becomes progressively simpler along with increasing temperature. Stress and strain are covered within Properties of Metals, Module 2, and creep is covered in Module 5, Plant Materials.
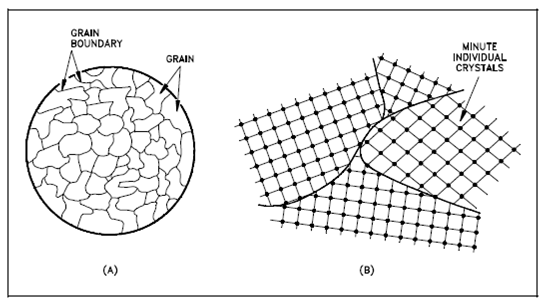
Figure: Grains and Boundaries
(a) Microscopic (b) Atomic