Pathway:
The basics steps in glycolysis are described below.
1. Glucose is phosphorylated through ATP to form glucose 6-phosphate, ADP and reaction is catalyzed through the enzyme hexokinase.
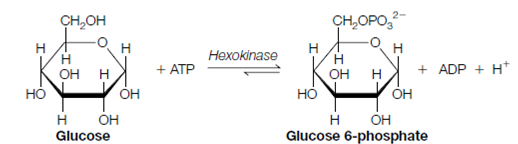
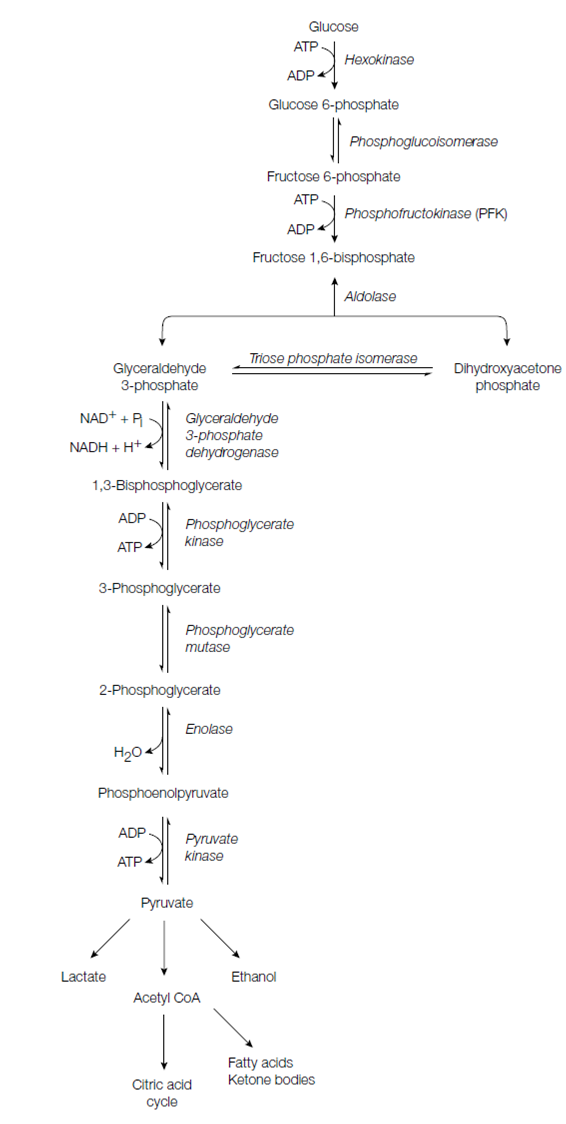
Figure: The reactions of glycolysis (glucose to pyruvate) plus fates of pyruvate.
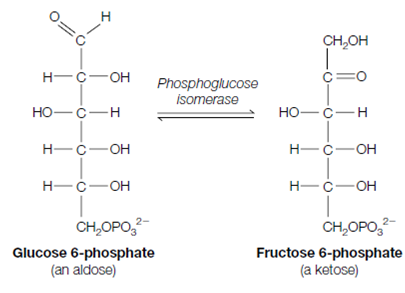
2. Glucose 6-phosphate is converted to fructose 6-phosphate through phosphoglucoisomerase.
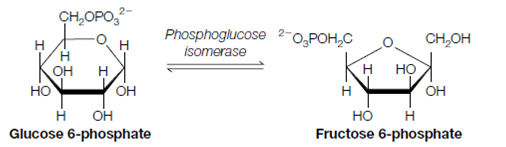
This isomerization includes the conversion of an aldose to a ketose, a conversion which is better seen through viewing the open chain representations of these molecules.
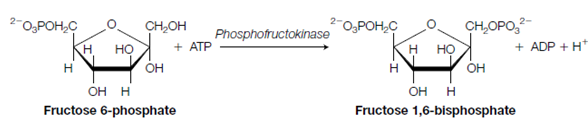
3. Fructose 6-phosphate is phosphorylated by ATP to form fructose 1,6- bisphosphate and ADP. Enzyme catalyzing this step is phosphofruc- tokinase (PFK).
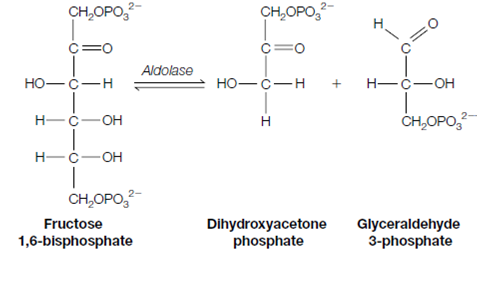
4. Aldolase splits fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate a six-carbon molecule into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate two three-carbon molecules, and dihydroxyacetone phosphate.
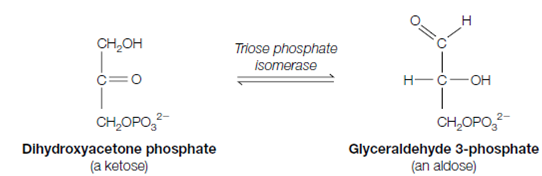
5. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate is the only molecule which can be used for the rest of glycolysis. Moreover, the dihydroxyacetone phosphate evaluate in the before step can rapidly be converted to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate through triose phosphate isomerase. That is an equilibrium reaction; as the glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate is used through the rest of glycolysis, more dihydroxyace- tone phosphate is transformed to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate as replacement. Therefore effectively, for each molecule of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate which is cleaved in step 4 two molecules of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate continue down the pathway.
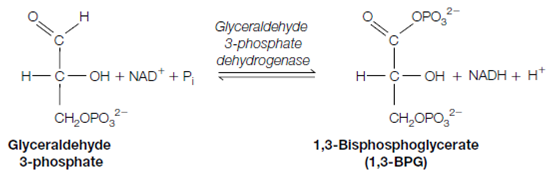
6. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate is converted to 1 3-bisphosphoglycerate. The reaction is catalyzed by glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase and uses inorganic phosphate and NAD+ . The other product is NADH. The energy for creating this new high-energy phosphate bond comes from the oxidation of the aldehyde group of the glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.
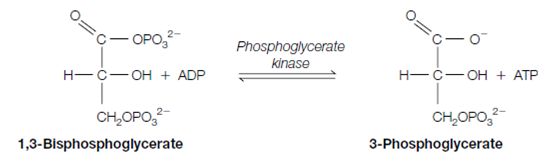
7. The newly established high-energy phosphate bond of 1 and 3-bisphosphoglycerate is now used to synthesize the ATP. A Phosphoglycerate kinase catalyzes the transfer of the phosphoryl group from the 1 and 3-bisphosphoglycerate to ADP and generating ATP and 3-phosphoglycerate.
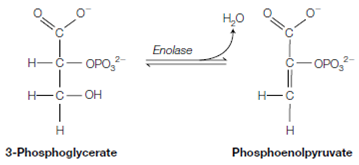
8. 3-Phosphoglycerate is converted to 2-phosphoglycerate through phosphoglycerate mutase. Therefore the reaction is a movement of the phosphate group to a variant carbon atom within the same molecule.
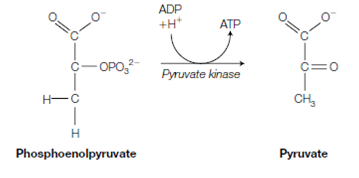
9. Enolase catalyzes the dehydration of 2-phosphoglycerate to create PEP (phosphoenolpyruvate). This reaction converts the low-energy phosphate ester bond of 2-phosphoglycerate into the high-energy phosphate bond of phosphoenolpyruvate.
10. In the last reaction, pyruvate kinase catalyzes the physiologically irreversible transfer of the phosphoryl group to form ATP and pyruvate from PEP to ADP.