Transport of oxaloacetate:
Pyruvate carboxylase is a mitochondrial matrix enzyme while the other enzymes of gluconeogenesis are situated outside the mitochondrion. Therefore oxaloacetate are produced through pyruvate carboxylase, requires exiting the mitochondrion. Moreover, the inner mitochondrial membrane is not permeable to this compound. Therefore oxaloacetate is converted to malate inside the mitochondrion through mitochondrial malate dehydrogenase, the malate is transported by the mitochondrial membrane through a special transport protein and then the malate is converted back to oxaloacetate in the cytoplasm through a cytosolic malate dehydrogenase.
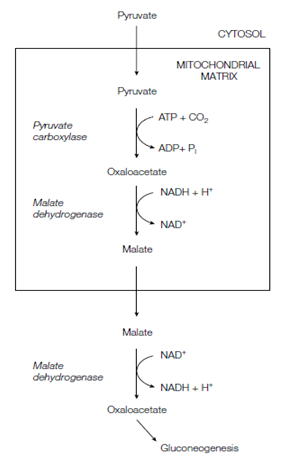
Figure: Transport of oxaloacetate out of the mitochondrion.